cervical spine test compression|cervical compression test physical therapy : fabrication When performing an assessment it is important to know if the tool you are using is measuring what you want to measure that is Specificity and how good it is correctly identifying a pattern that is Sensitivityas both contribute to the diagnostic accuracy . See more webToday's matches. Explore daily matchups and click a match to simulate. Match Simulator - Immerse yourself in the excitement of soccer. Effortlessly simulate any soccer match or cup with Match Simulator.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Newfoundland And Labrador Online Casinos. How to Evaluate Any Newfoundland and Labrador Online Casino. Choosing the Best Newfoundland Online Casino. Games at Newfoundland Casinos. Popular Payment Methods in Newfoundland Online Casinos. Our Team of Gambling Experts. FAQ about Newfoundland and Labrador Online .
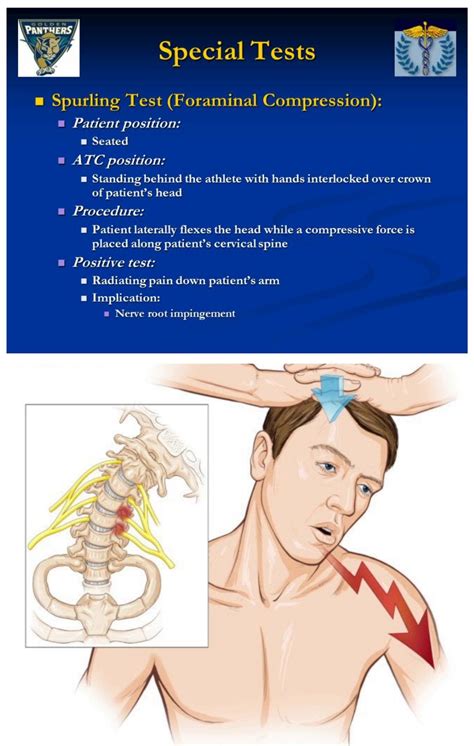
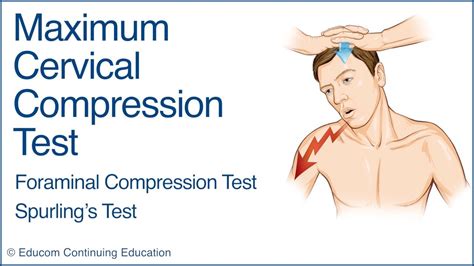
The Spurling's test (also known as Maximal Cervical Compression Test and Foraminal Compression Test) is used during a musculoskeletal assessment of the cervical spine when looking for cervical nerve root compression causing Cervical Radiculopathy. See moreThere are different ways described in the literature to perform the Spurling's test. The version that provoked arm symptoms the best was with the . See moreAlthough this test is commonly used for assessing cervical radiculopathy it is important due to its lower sensitivity that other tests are used in conjunction. In 2003, Dr. Robert . See moreWhen performing an assessment it is important to know if the tool you are using is measuring what you want to measure that is Specificity and how good it is correctly identifying a pattern that is Sensitivityas both contribute to the diagnostic accuracy . See more
De Hertogh WJ, Vaes PH, Vijverman V, De Cordt A, Duquet W. The clinical examination of neck pain patients: The validity of a group of tests.Manual Therapy. 2007; 12 (1): 50-5. Tong HC, Haig AJ, Yamakawa K. The Spurling test and cervical . See moreThis category contains pages that relate to special tests. Pages in category "Cervical Spine - Special Tests". The following 11 pages are in this category, out of 11 total. B. Bakody Sign. C. .neck pain with radiating pain/cervical radiculopathy, including the upper limb tension test, Spurling's test, distraction test, and the Valsalva test. Cranial cervical flexion and neck flexor muscle endurance tests may be use in .Spurling’s Test for Cervical Radicular Syndrome / Cervical Radiculopathy. Spurling’s test is a test with a low sensitivity of 50% and a good specificity of 83% to diagnose cervical radicular syndrome according to Wainner et al. .
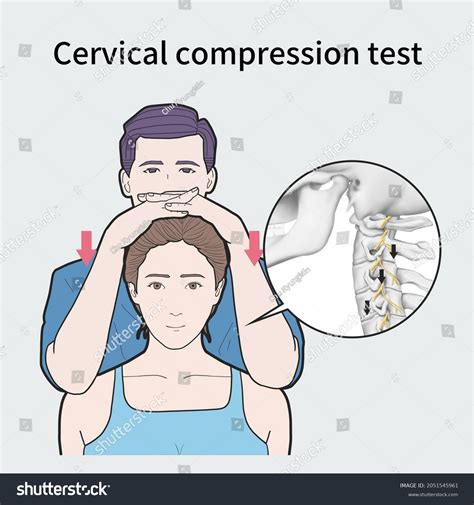
What is the Spurling test? The Spurling test is a physical assessment to diagnose cervical radiculopathy or a pinched nerve in your neck. If you experience neck pain, a healthcare provider may offer this test.The Spurling test can tell your provider if something is squeezing or pressing against a nerve (nerve root compression) in your cervical spine. The Maximum Cervical compression test is used to detect nerve root involvement in the cervical spine. This test is also known by other names, including the Foraminal Compression test and Spurling’s test. This test should not be used if a significant cervical injury is suspected. Cervical radiculopathy happens when a nerve root in your neck (cervical spine) becomes compressed (pinched) and inflamed. This compression has two main causes: Degenerative changes that happen in your spine as you age (cervical spondylosis). A herniated (bulging) disk in your neck. Cervical spondylosis and cervical radiculopathy
Spinal cord compression can occur anywhere along your spine. Symptoms include numbness, pain, and weakness. . (cervical spine) down to your lower back (very top of lumbar spine). . (EMG), an electrical test of muscle activity. How is spinal cord compression treated? The medical team involved in treating your spinal cord compression may . Cervical Myelopathy is a common form of neurologic impairment caused by compression of the cervical spinal cord most commonly due to degenerative cervical spondylosis. . test is positive when extreme cervical flexion leads to electric shock-like sensations that radiate down the spine and into the extremities. Evaluation.Pages in category "Cervical Spine - Special Tests" The following 11 pages are in this category, out of 11 total. B. Bakody Sign; C. Canadian C-Spine Rule; Cervical Distraction Test; Cervical Flexion-Rotation Test; Cervical rotation lateral flexion test; Cranio‐cervical Flexion Test; H. Hoffmann's Sign; S. Sharp Purser Test; Spurling's Test; T.
Cervical stenosis is one such degenerative condition that may affect the spinal cord and lead to compromised coordination of the extremities. When diagnosing cervical stenosis, doctors must determine whether progressive dysfunction (myelopathy) is present as a result of the spinal cord compression. See Cervical Stenosis with Myelopathy Spinal cord compression—also called cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM)— is caused by any condition that puts pressure on the spinal cord. Symptoms may develop suddenly or gradually and may include pain or stiffness in the neck or back, balance issues, or a burning pain in the arms or legs . cervical spine C6 nerve root travels under C5 pedicle (mismatch) lumbar spine L5 nerve root travels under L5 pedicle (match) . foraminal compression test that is specific, but not sensitive, in diagnosing acute radiculopathy. performed by rotating head toward the affected side, extending the neck, and then applying and axial load (downward . Cervical Spine Tests That Provide or Relieve Pain Spurling Neck Compression Test . Spurling and Scoville first described the Spurling neck compression test, also known as the foraminal compression test, neck compression test, or quadrant test, in 1944 as “the most important diagnostic test and one that is almost pathognomonic of a cervical intraspinal lesion.”
what is deep neck compression
This test works when your doctor flexes your cervical spine. If you feel a shock-like pain or feeling down your spine or arms and legs, you’ll get a positive test. Hoffman’s sign.in the diagnosis of cervical radiculopathy. Questions/Purposes We assessed the ability of six known variations of the Spurling test to reproduce the complaints of patients diagnosed with cervical radiculopathy. Methods We prospectively enrolled 67 patients presenting with cervical radicular-like symptoms and concordant radiographic findings. Each patient underwent six ."Cervical radiculopathy is a disease process marked by nerve compression from herniated disk material or arthritic bone spurs. This impingement typically produces neck and radiating arm pain or numbness, sensory deficits, or motor . Thank you for following @OrthoEvalPal Today I will show you how to perform the Cervical Compression Test correctly and what you should see in a positive tes.
The test is positive for cervical radiculopathy with reproduction or increase of symptoms with contralateral cervical side bending, or with a decrease in symptoms with ipsilateral side bending.
Figure 6. Foraminal compression test to assess for a space occupying condition of the cervical spine. (A) The therapist places downward pressure on the client’s head while the client’s neck and head are in a neutral position. (B) Maximal foraminal compression test to the right side of the client’s body.
This page provides a step-by-step overview of the key elements of the cervical spine evaluation, including the subjective assessment (history taking) and the objective assessment (observation and tests). . Cervical Compression Test: pain with this test may indicate an intervertebral disc issue, vertebral fracture, or nerve root irritation (if . Flexion compression test. Procedure: The patient is seated. The examiner stands behind the patient and passively moves the cervical spine into flexion (tilts the patient’s head forward). Then axial compression is applied to the top of the head. Assessment: This is a good test of the integrity of the intervertebral disk.
The Spurling test is valuable in diagnosing cervical nerve compression and radiculopathy, aiding in the identification of specific spinal levels and nerves involved. It can help differentiate nerve root impingement from other causes of neck and arm pain, such as muscular strains or joint dysfunction.Cervical spinal cord compression . These tests help determine ongoing nerve damage and the site of nerve compression. Myelogram. This imaging test examines the relationship between your vertebrae and disks, outlines the spinal cord and nerves exiting your spinal column. It shows if such possible things as a tumor, bone spurs or herniated disk .

Cervical radiculopathy is a clinical condition characterized by unilateral arm pain, numbness and tingling in a dermatomal distribution in the hand, and weakness in specific muscle groups associated with a single cervical nerve root. It is caused by nerve root compression in the cervical spine either from degenerative changes or from an acute soft disc hernation.
Relief of compression. Treatment of spinal cord compression is directed at relieving pressure on the cord. Incomplete or very recent complete loss of function may be reversible, but complete loss of function rarely is; thus, for acute compression, diagnosis and treatment must occur immediately. Surgery is indicated in the following cases:
The Spurling test, also known as the Spurling maneuver, is a physical examination technique used to help diagnose cervical radiculopathy, which is a condition in which a nerve in the neck is compressed or irritated, leading to pain, numbness, and weakness in the arm or hand.. To perform the Spurling test, the examiner stands behind the seated patient and then extends . Impaired gait is one of the cardinal symptoms of degenerative cervical myelopathy (DCM) and frequently its initial presentation. Quantitative gait analysis is therefore a promising objective tool in the disclosure of early cervical cord impairment in patients with degenerative cervical compression. Cervical spine canal stenosis, whether of bony or soft-tissue origins, can cause lower-extremity signs and symptoms. Most notable is long tract pain, or rhizalgia, appearing in an ipsilateral leg . Spurling compression test: Dural sheath, nerve root, spinal nerve: Radicular pain: Maximal foraminal compression test: Dural sheath, nerve root .
vochtmeter steen huren
special test for cervical spine
Try these featured games or explore thousands of others on .
cervical spine test compression|cervical compression test physical therapy